Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (34): 5545-5551.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.34.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Decellularized liver scaffold’s preparation and recellularization: how far is the bioartificial liver from clinical practice?
- Affiliated Calmette Hospital of Kunming Medical University/First Hospital of Kunming, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2017-07-11Online:2017-12-08Published:2018-01-04 -
Contact:Zhang Lei, Ph.D., Senior researcher, Affiliated Calmette Hospital of Kunming Medical University/First Hospital of Kunming, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Su Wen-jun, Master, Research intern, Biomedical Research Center, Affiliated Calmette Hospital of Kunming Medical University/First Hospital of Kunming, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China in 2017, No. 81660303
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Su Wen-jun, Zhang Lei.
share this article
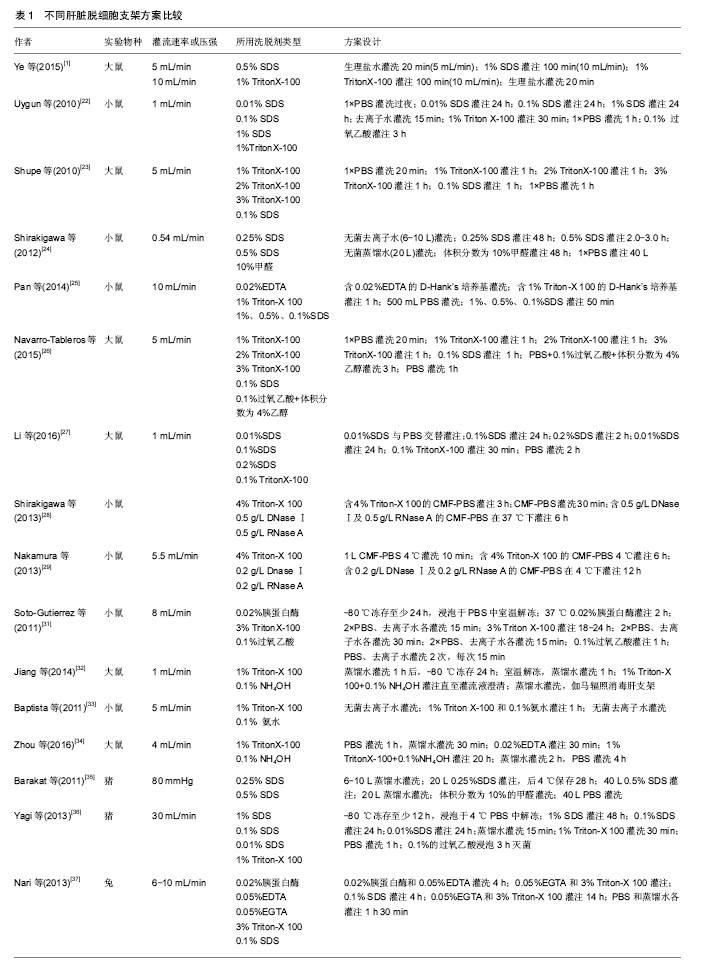
2.1 细胞外基质与3D肝脏脱细胞支架 3D肝脏脱细胞支架之所以能够发挥天然生物支架的优良特性,得益于其上保留的细胞外基质成分。细胞外基质主要由胶原蛋白、层粘连蛋白、纤连蛋白、蛋白多糖和糖蛋白等组成,由此构成的动态微环境具有器官特异性能[12],包括物理性能(细胞极性、细胞分裂、迁移)[13]、生物化学性能(细胞信号传导)[12-14]、生物力学性能,不仅如此,其上所特有的细胞生长因子和生物诱导因子为细胞黏附、组织重构提供了支持[14-15];另一方面,脱细胞后的细胞外基质不含细胞或DNA、alpha-Gal等可产生免疫原性的分子,很大程度上避免了移植后的免疫排斥反应[16]。 对于具体的肝脏而言,可根据肝门管区血管和中心静脉血管分布将肝脏细胞外基质分为门静脉区域和中心周围区域,不同区域所含的蛋白成分不同[17],肝脏内皮细胞通过整合素受体蛋白与周围的细胞外基质产生信号联系,即当整合素受到激活,就会触发细胞外基质上相关的化学、机械性能信号通路从而影响细胞生理周期、形态及运动[18]。研究发现经整合素识别位点系列多肽(RGD肽)固定的脱细胞支架黏附性增加,且可促进细胞生长和胶原分泌[19],这提示探索整合素与脱细胞支架之间的关系将有利于脱细胞支架的再细胞化及临床应用。 2.2 肝脏脱细胞支架的制备 制备3D肝脏脱细胞支架即利用物理方法、化学方法或酶消化法从肝脏中去除细胞成分和遗传物质,同时尽可能地保存其原本的细胞外基质结构及其生物学活性。为了优化脱细胞的过程,需要考虑洗脱试剂、灌流方法和脱细胞流程等因素(表1)。 "
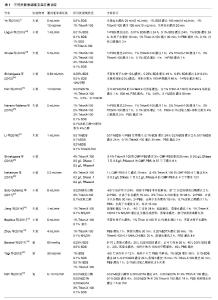
洗脱剂的选择对整个制备流程至关重要,不同洗脱剂的洗脱效果及其对细胞外基质结构产生的影响不同。一般来说,离子型洗脱剂(如SDS)的洗脱效果要明显优于非离子型洗脱剂(如TritonX-100),但对细胞外基质的损伤程度较大[20]。其他洗脱试剂如酶类(胰蛋白酶、核酸酶等),虽能够特异性地去除细胞不同成分,但单独使用洗脱效果不佳[21]。若通过设置不同的浓度梯度[22-27]、联合使用非离子型洗脱剂及核酸酶[28-29],能够加强洗脱效果,很好地实现支架的去细胞化;此外,通过其他物理方法如冻融法也能对脱细胞起到很好的辅助作用[30-32],但需注意冻融的时间和次数。 在灌流过程中,灌流所需时间及流速设计至关重要,通常两者能影响支架制备的总体时间及效果,因此在脱细胞方案设计过程中需综合考虑支架组织特点及选用洗脱试剂类型[33-34],在脱细胞的同时很好地保存了支架超微结构的完整性。 2.3 肝脏脱细胞支架的鉴定及评价 全肝脏器官经不同洗脱方法去细胞后,整个肝脏大体外观得以完整保留,呈白色半透明样,通过肝包膜,可清晰地观察到血管、胆管等结构(图1)。然而,仅仅只是通过宏观的大体观察不足以说明去细胞化的程度,还需进一步运用微观的鉴定方法:①细胞外基质相关蛋白检测:脱细胞后对细胞外基质上存留的胶原蛋白、层粘连蛋白、纤维蛋白等进行定性或定量检测[22-26,28,31-35],以此判断细胞外基质脱细胞后蛋白结构的保留情况;②生长因子含量检测:对脱细胞后细胞外基质上的成纤维生长因子、血管内皮生长因子、肝细胞生长因子等进行定量检测或活性鉴 定[29,31];③残留DNA含量检测:目前广泛使用的鉴定标准包括每毫克(干质量)细胞外基质中DNA含量小于50 ng;DNA 片段长度小于200 bp;支架切片经苏木 精-伊红染色或DAPI 染色后未见细胞核[9,29,31-32,34-35];④血管脉网结构鉴定:细胞外基质上血管网络的保存对于3D脱细胞支架在体内移植后的融合及再内皮化起至关重要的作用,利用血管铸型技术,可以观察到脱细胞后的血管结构完整无缺[24-25,34-35];⑤血管脉网显微结构观察:通过电镜观察脱细胞后细胞外基质上细胞残留和血管保留情况[22,24-25,31,34,38]。总而言之,对于肝脏脱细胞支架评价,需要从去细胞效率及细胞外基质保存两个大的方向出发,可根据实验具体需要制定合适的鉴定方案。 2.4 肝脏脱细胞支架的再细胞化 2.4.1 种子细胞 制备肝脏脱细胞支架的最终目的即进行支架的再细胞化,一般利用该脱细胞支架自身脉管结构将细胞输送到支架对应的实质部分,重新植入的细胞可在支架内分布、迁移、存活,并发挥特定功能。目前用于再细胞化的种子细胞主要包括:①胎肝细胞:临床研究发现胎肝细胞对于终末期肝病有一定疗效[36],其涉及的伦理、免疫排斥、细胞增殖等问题限制了胎肝细胞的应用;②肝细胞:人肝细胞免疫并发症少,通过门静脉将肝细胞注入脱细胞支架,移植率高,且能维持原有肝细胞功能[31-33],但由于来源有限,体外增殖困难[37-38],现已有研究者试图利用基因工程技术让原代肝细胞成为永生化细胞系[39];③诱导性多能干细胞:诱导性多能干细胞对于干细胞应用来说是一个巨大突破,它避免了胚胎干细胞涉及的伦理以及免疫排斥等问题,诱导性多能干细胞经定向诱导可以向肝细胞分化且在肝衰竭实验小鼠体内发挥肝细胞功能[40-42],甚至可以作为心脏脱细胞支架的再细胞化种子细胞[43],但诱导性多能干细胞存在的诸如致瘤、基因突变等问题尚待解决[44];④人肝癌细胞:HepG2、C3A细胞能在体外大量扩增,且具有表达肝细胞相关蛋白的功能,是制作生物人工肝的常用种子细胞来源[45],但由于其致瘤性问题,限制了其临床应用;⑤间充质干细胞:间充质干细胞能够从骨髓、脐带等多种成体组织中获得,可在体外快速增殖,具有多向分化潜能,加之其在宿主组织中免疫原性低,在组织工程特别是利用间充质干细胞进行肝病治疗上有着巨大的潜力[46-47]。有研究显示,肝脏脱细胞支架中富有的多种细胞因子可促进间充质干细胞向肝细胞分化,分化后得到的肝样细胞具有与肝细胞相似的细胞超微结构与功能特性[48]。由此,可以认为间充质干细胞较其他干细胞而言是一种更加优良的生物人工肝种子细胞。 2.4.2 细胞植入方式及数量 肝脏脱细胞支架的再细胞化是极其精密的过程,不同的移植方法、移植通道、细胞数目均会对再细胞化效果产生影响。总体来说,再细胞化可通过薄壁组织直接注射、分步灌注以及连续灌注的方法实现,其中分步灌注法更易于细胞在支架内的迁移和分布,移植率显著提高[31],且能有效避免血栓等并发症[22]。另外,需严格控制移植细胞量,一般接种量以(5-10)×107为最佳,数量过大会导致移植过程中种子细胞因密度过大而死亡,且容易堵塞支架脉管系统,进而影响再细胞化的最终效果[49-51]。 2.4.3 细胞动态培养 研究者们利用肝脏脱细胞支架制定一套体外连续灌注培养系统,通过控制不同的流体流速为再植入的种子细胞提供优良的体外生存环境。Lang等[52]将人肝细胞系HepG2植入猪肝脱细胞支架中,细胞在其中繁殖并表达肝细胞功能;Wang等[53]发现人肝干细胞在大鼠肝脏脱细胞支架上存活时间长达8周,支架特有的仿生环境更有利于诱导干细胞向成熟肝细胞分化;Butter等[54]发现移植后的肝细胞在24 h内从血管网络中迁移,并向周围的薄壁组织聚集,移植后3D脱细胞支架较2D培养而言显示出更强的肝功能特性;Park等[55]证实脱细胞肝脏支架上含有的肝细胞生长因子能够促进诱导性多能干细胞向肝细胞分化;Jiang等[56]在肝脏脱细胞支架中诱导小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向肝细胞分化,肝样细胞可表达更多的肝细胞相关蛋白标记。 2.5 动物实验及临床应用 2.5.1 动物实验 将细胞植入肝脏脱细胞支架后,细胞在支架内存活,发挥肝脏相关的特异性功能,整个生物人工肝逐渐趋于成熟,随后将其移植入实验动物体内,是生物人工肝技术向临床应用转化的关键步骤。Uygun等[22]首次对再细胞化人工肝进行异位移植,将小鼠单侧右肾切除,然后将肾动、静脉连接植入肝脏的门静脉与腔静脉,开放主动脉,发现整个支架有了血供,通过Tunnel染色发现肝脏支架成活了8 h;Bao等[49]将人工肝原位移植到部分肝切除的大鼠体内,显著延长了肝切除鼠的生存期;Park等[55]对移植后的大鼠给予全身肝素支持,但一两个小时后支架内出现了凝血现象。一系列的动物实验表明,再细胞化生物人工肝可移植到同种或异种动物体内,对受体发挥短暂的代偿功能,但支架在移植后数小时内均发现凝血,到目前为止,还没有任何实验表明生物人工肝在移植后能维持持续血供[22,33,57],这可能是由于其不能很好地适应宿主环境,从而无法耐受免疫排斥反应,除此之外,手术过程中血管缝合缺陷、自我血管重构失败而造成血栓、缺血再灌注等,也是造成人工肝在宿主内存活时间短的原因[51]。值得一提的是,大动物肝脏脱细胞支架的制备及临床研究受到越来越多的关注,特别是利用猪肝脱细胞支架制成的生物人工肝进行异体移植,具有低免疫原性的优点,可在将来生物医学临床研究中发挥巨大潜能[58-60]。 2.5.2 药物筛查 在新药研发的早期阶段,利用体外肝毒性药物筛选模型可以显著节约成本,同时也减少动物实验的需要。不同于体内模型,体外模型可以很好地控制实验条件从而更灵敏和准确地解读药物诱导的肝损伤机制[61]。通常来讲,90%的药物由肝细胞CYP450代谢,因此原代肝细胞培养是实现体外肝毒性药物筛选的关键。较2D培养系统而言,3D肝脏脱细胞支架可以促进细胞-细胞与细胞-基质的相互作用以及肝细胞的分化,加之灌注培养能够提高肝细胞的生存能力,其中的剪切应力和流体流速还能刺激肝细胞解毒基因表达上调,就此而言,3D肝脏脱细胞支架是一种强大的药物高通量筛选体外模型[62-63]。"
| [1]Ye JS, Stoltz JF, de Isla N, et al. An approach to preparing decellularized whole liver organ scaffold in rat. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;25(1 Suppl):159-166.[2]Fuhrman C, Jougla E, Nicolau J, et al. Deaths from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in France, 1979-2002: a multiple cause analysis. Thorax. 2006;61(11):930-934.[3]Strong RW. Liver transplantation: current status and future prospects. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 2001;46(1):1-8.[4]Carpentier B, Gautier A, Legallais C. Artificial and bioartificial liver devices: present and future. Gut. 2009;58(12): 1690-1702.[5]Allen JW, Hassanein T, Bhatia SN. Advances in bioartificial liver devices. Hepatology. 2001;34(3):447-455.[6]Struecker B, Raschzok N, Sauer IM. Liver support strategies: cutting-edge technologies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11(3):166-176.[7]Bañares R, Catalina MV, Vaquero J. Liver support systems: will they ever reach prime time. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2013;15(3):312.[8]Badylak SF. The extracellular matrix as a biologic scaffold material. Biomaterials. 2007;28(25):3587-3593.[9]Crapo PM, Gilbert TW, Badylak SF. An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials. 2011; 32(12):3233-3243.[10]Faulk DM, Carruthers CA, Warner HJ, et al. The effect of detergents on the basement membrane complex of a biologic scaffold material. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1):183-193.[11]Badylak SF, Taylor D, Uygun K. Whole-organ tissue engineering: decellularization and recellularization of three-dimensional matrix scaffolds. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2011;13:27-53.[12]Gattazzo F, Urciuolo A, Bonaldo P. Extracellular matrix: a dynamic microenvironment for stem cell niche. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(8):2506-2519.[13]Lu P, Weaver VM, Werb Z. The extracellular matrix: a dynamic niche in cancer progression. J Cell Biol. 2012; 196(4):395-406.[14]Watt FM, Huck WT. Role of the extracellular matrix in regulating stem cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(8): 467-473.[15]Hynes RO. The extracellular matrix: not just pretty fibrils. Science. 2009;326(5957):1216-1219.[16]Lee SY, Kim HJ, Choi D. Cell sources, liver support systems and liver tissue engineering: alternatives to liver transplantation. Int J Stem Cells. 2015;8(1):36-47.[17]Susick R, Moss N, Kubota H, et al. Hepatic progenitors and strategies for liver cell therapies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001; 944:398-419.[18]Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110(6):673-687.[19]史嘉玮,董念国,孙宗全,等.RGD肽固定对组织工程心脏瓣膜构建的作用[J].临床急诊杂志,2006,7(3):100-103.[20]Mattei G, Di Patria V, Tirella A, et al. Mechanostructure and composition of highly reproducible decellularized liver matrices. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(2):875-882.[21]邬迪,王志伟.脱细胞技术及其在肝脏组织工程中的应用[J].江苏医药,2014,40(18):2176-2179.[22]Uygun BE, Soto-Gutierrez A, Yagi H, et al. Organ reengineering through development of a transplantable recellularized liver graft using decellularized liver matrix. Nat Med. 2010;16(7):814-820.[23]Shupe T, Williams M, Brown A, et al. Method for the decellularization of intact rat liver. Organogenesis. 2010;6(2): 134-136. [24]Shirakigawa N, Ijima H, Takei T. Decellularized liver as a practical scaffold with a vascular network template for liver tissue engineering. J Biosci Bioeng. 2012;114(5):546-551.[25]Pan MX, Hu PY, Cheng Y, et al. An efficient method for decellularization of the rat liver. J Formos Med Assoc. 2014;113(10):680-687.[26]Navarro-Tableros V, Herrera Sanchez MB, Figliolini F, et al. Recellularization of rat liver scaffolds by human liver stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(11-12):1929-1939.[27]Li Q, Uygun BE, Geerts S, et al. Proteomic analysis of naturally-sourced biological scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2016;75: 37-46.[28]Shirakigawa N, Takei T, Ijima H. Base structure consisting of an endothelialized vascular-tree network and hepatocytes for whole liver engineering. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013;116(6):740-745.[29]Nakamura S, Ijima H. Solubilized matrix derived from decellularized liver as a growth factor-immobilizable scaffold for hepatocyte culture. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013; 116(6): 746-753.[30]Keane TJ, Swinehart IT, Badylak SF. Methods of tissue decellularization used for preparation of biologic scaffolds and in vivo relevance. Methods. 2015;84:25-34.[31]Soto-Gutierrez A, Zhang L, Medberry C, et al. A whole-organ regenerative medicine approach for liver replacement. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(6):677-686.[32]Jiang WC, Cheng YH, Yen MH, et al. Cryo-chemical decellularization of the whole liver for mesenchymal stem cells-based functional hepatic tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2014;35(11):3607-3617.[33]Baptista PM, Siddiqui MM, Lozier G, et al. The use of whole organ decellularization for the generation of a vascularized liver organoid. Hepatology. 2011;53(2):604-617.[34]Zhou P, Huang Y, Guo Y, et al. Decellularization and Recellularization of Rat Livers With Hepatocytes and Endothelial Progenitor Cells. Artif Organs. 2016;40(3):E25-38.[35]Lee JS, Shin J, Park HM, et al. Liver extracellular matrix providing dual functions of two-dimensional substrate coating and three-dimensional injectable hydrogel platform for liver tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(1): 206-218.[36]Yagi H, Parekkadan B, Suganuma K, et al. Long-term superior performance of a stem cell/hepatocyte device for the treatment of acute liver failure. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009; 15(11):3377-3388.[37]Miranda JP, Leite SB, Muller-Vieira U, et al. Towards an extended functional hepatocyte in vitro culture. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2009;15(2):157-167.[38]March S, Hui EE, Underhill GH, et al. Microenvironmental regulation of the sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype in vitro. Hepatology. 2009;50(3):920-928.[39]何宏亮,李建国,高志良.人工肝和干细胞在肝衰竭治疗中的进展[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2013,29(9):670-673.[40]Si-Tayeb K, Noto FK, Nagaoka M, et al. Highly efficient generation of human hepatocyte-like cells from induced pluripotent stem cells. Hepatology. 2010;51(1):297-305.[41]Espejel S, Roll GR, McLaughlin KJ, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes have the functional and proliferative capabilities needed for liver regeneration in mice. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(9):3120-3126.[42]Behbahan IS, Duan Y, Lam A, et al. New approaches in the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells toward hepatocytes. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(3):748-759.[43]Lu TY, Lin B, Kim J, et al. Repopulation of decellularized mouse heart with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiovascular progenitor cells. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2307.[44]Ebben JD, Zorniak M, Clark PA, et al. Introduction to induced pluripotent stem cells: advancing the potential for personalized medicine. World Neurosurg. 2011;76(3-4): 270-275.[45]Liu H, You S, Rong Y, et al. Newly established human liver cell line: a potential cell source for the bioartificial liver in the future. Hum Cell. 2013;26(4):155-161.[46]Zhang L, Zhao YH, Guan Z, et al. Application potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton's jelly in liver tissue engineering. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;25(1 Suppl): 137-143.[47]Allameh A. Recent technological advances in hepatogenic differentiation of stem cells relevant to treatment of liver diseases. Int J Pediatr. 2014;2(2):20.[48]Zhou Q, Li L, Li J. Stem cells with decellularized liver scaffolds in liver regeneration and their potential clinical applications. Liver Int. 2015;35(3):687-694.[49]Bao J, Shi Y, Sun H, et al. Construction of a portal implantable functional tissue-engineered liver using perfusion-decellularized matrix and hepatocytes in rats. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(5):753-766.[50]Zhou P, Lessa N, Estrada DC, et al. Decellularized liver matrix as a carrier for the transplantation of human fetal and primary hepatocytes in mice. Liver Transpl. 2011;17(4):418-427.[51]Caralt M, Velasco E, Lanas A, et al. Liver bioengineering: from the stage of liver decellularized matrix to the multiple cellular actors and bioreactor special effects. Organogenesis. 2014;10(2):250-259.[52]Lang R, Stern MM, Smith L, et al. Three-dimensional culture of hepatocytes on porcine liver tissue-derived extracellular matrix. Biomaterials. 2011;32(29):7042-7052.[53]Wang Y, Cui CB, Yamauchi M, et al. Lineage restriction of human hepatic stem cells to mature fates is made efficient by tissue-specific biomatrix scaffolds. Hepatology. 2011;53(1): 293-305.[54]Butter A, Aliyev K, Hillebrandt KH, et al. Evolution of graft morphology and function after recellularization of decellularized rat livers. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016 Dec 13. doi: 10.1002/term.2383. [Epub ahead of print][55]Park KM, Hussein KH, Hong SH, et al. Decellularized Liver Extracellular Matrix as Promising Tools for Transplantable Bioengineered Liver Promotes Hepatic Lineage Commitments of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(5-6):449-460.[56]Jiang WC, Cheng YH, Yen MH, et al. Cryo-chemical decellularization of the whole liver for mesenchymal stem cells-based functional hepatic tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2014;35(11):3607-3617.[57]Barakat O, Abbasi S, Rodriguez G, et al. Use of decellularized porcine liver for engineering humanized liver organ. J Surg Res. 2012;173(1):e11-25.[58]Yagi H, Fukumitsu K, Fukuda K, et al. Human-scale whole-organ bioengineering for liver transplantation: a regenerative medicine approach. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(2): 231-242.[59]Barakat O, Abbasi S, Rodriguez G, et al. Use of decellularized porcine liver for engineering humanized liver organ. J Surg Res. 2012;173(1):e11-25.[60]Nari GA, Cid M, Comín R, et al. Preparation of a three-dimensional extracellular matrix by decellularization of rabbit livers. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2013;105(3):138-143.[61]Damania A, Jain E, Kumar A. Advancements in in vitro hepatic models: application for drug screening and therapeutics. Hepatol Int. 2014;8(1):23-38.[62]Guzzardi MA, Domenici C, Ahluwalia A. Metabolic control through hepatocyte and adipose tissue cross-talk in a multicompartmental modular bioreactor. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(11-12):1635-1642.[63]Schmelzer E, Triolo F, Turner ME, et al. Three-dimensional perfusion bioreactor culture supports differentiation of human fetal liver cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(6):2007-2016.[64]Mazza G, Rombouts K, Rennie Hall A, et al. Decellularized human liver as a natural 3D-scaffold for liver bioengineering and transplantation. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13079. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Li Xuan, Sun Yimin, Li Longbiao, Wang Zhenming, Yang Jing, Wang Chenglin, Ye Ling. Manufacturing of nano-modified polycaprolactone microspheres and its biological effects in dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1530-1536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||